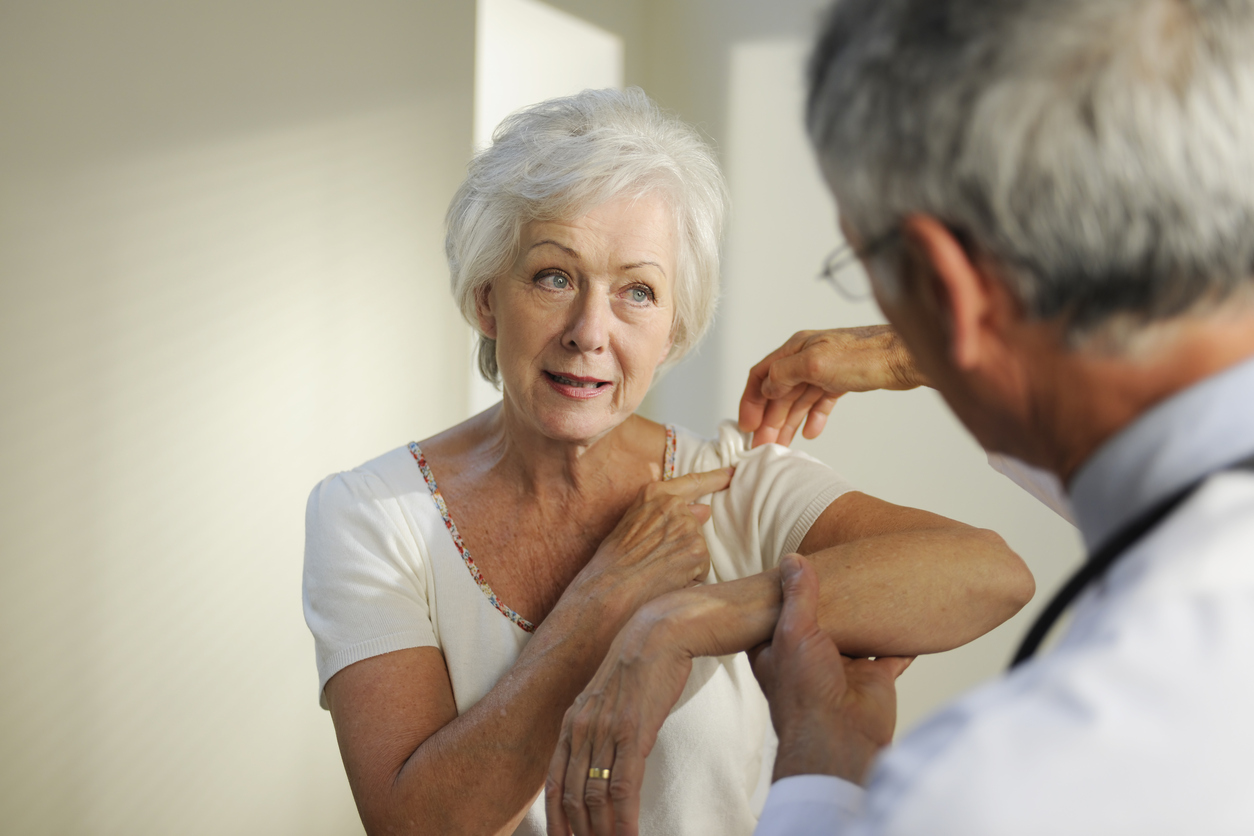
Shoulder surgery is a complex procedure with many different types. It can be scary to think about the process and its meaning. However, knowing more about shoulder surgery will likely put your mind at ease so you can better prepare for what lies ahead.
Remember to vet your orthopedic doctor thoroughly and if you need a good example of an excellent practice go ahead and check out Integrated Orthopedics.
Overview of Shoulder Surgery
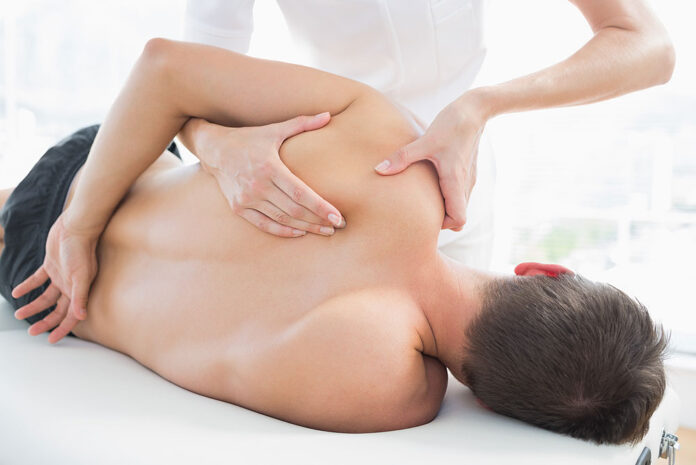
Total shoulder replacement is one of the most common forms of shoulder surgery. It is used to treat arthritis and repair damage to the shoulder. It may also fix the shoulder after trauma, such as a hockey injury.
Rotator cuff repair is usually needed when a tear in the rotator cuff cannot be healed with other therapy options. The rotator cuff consists of tendons that help with the shoulder’s stability when lifting heavy objects, throwing, and in sports like tennis.
Arthroscopy can be used for several types of injuries, such as torn meniscus in the knee or impingement syndrome in the shoulder (shoulder bursitis). In this surgery, a camera is inserted into the knee or shoulder, and a small surgical tool removes debris causing pain.
Acromioclavicular joint repair is an arthroscopic surgery. Doctors will insert a needle into the joint to create space for removing bone spurs that are causing pain and discomfort.
Complications of Shoulder Surgery

There can be numerous risks associated with shoulder surgery, including infections, blood clots, nerve damage, and injury to internal organs. In total shoulder replacement, complications can include a frozen shoulder and nerve damage.
In rotator cuff repair, the torn tendon cannot be completely repaired, which can cause the arm to be weaker than before the surgery.
Recovery Time
The recovery process after surgery varies depending on the surgery type and whether you have one or both shoulders operated on. You must wear a sling to keep your arm still during recovery. You may wear a cast afterward if it is determined that you will need more healing time.
The amount of time needed to recover varies greatly. Total shoulder replacement usually requires six to eight weeks before you can return to your regular routines. Rotator cuff repair may take up to twelve weeks because the torn tendon cannot be repaired.
Arthroscopy for a frozen shoulder typically takes about three weeks, but it can range between one and four weeks, depending on the amount of swelling. If a torn meniscus or inflammatory arthritis is treated with arthroscopic surgery, recovery will take as little as two days.
Physical Therapy

You will be given physical therapy after surgery to help you recover. Your doctor will also teach you to avoid injury while lifting heavy objects and doing sports.
The goal of the therapy is to restore function, which includes strength, movement, and flexibility. Physical therapy can last between three and six months to a year.
Pain Control and Medications
Pain control is essential during recovery from shoulder surgery. Your doctor will probably prescribe medication that will work best for you.
Therapy after Shoulder Surgery
Therapy is essential for shoulder surgery, as it helps reduce pain and regain shoulder motion. Therapy may include ultrasound therapy, electrical nerve stimulation, biofeedback, and cold laser.
You may need to visit a physical therapist for months after surgery to regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Shoulder surgery is a major operation. Even though it is not life-threatening, the procedure comes with many risks. So you must know what to expect before having your surgery done. Knowing the outcome after your surgery and its implications for your life is prudent.
Treatment of frozen Shoulder
A frozen shoulder is a painful condition that occurs when movement is restricted in the shoulder joint.
This causes inflammation and damage to the tendons and muscles, resulting in stiffness and decreased range of motion. It is often caused by a long-standing injury that has gone unrecognized for years.
Medline Plus: Frozen Shoulder

Frozen shoulder is a condition of the shoulder that can occur on both sides of the joint because of physical or emotional stress.
It is common for people to experience symptoms for many years before seeking help, believing that it is another type of arthritis or an inflamed bursa.
The Recovery Process
The recovery process after frozen shoulder surgery varies greatly depending on the type of surgery performed and whether you have one or both shoulders operated on. The following guide includes information on the recovery process after shoulder arthroscopy and arthroplasty.
The recovery process after frozen shoulder surgery differs from total shoulder replacement. It is used to treat arthritis, and the results usually could be better due to the longer recovery time.
Shoulder Arthroscopy/Arthroplasty
Shoulder arthroscopy involves making an incision into the joint to remove damaged tissue. Your doctor will insert a tiny camera through a small incision in the shoulder, then use surgical instruments inserted into the joint through smaller incisions to perform surgery.
This procedure aims to restore functionality to the joint by removing damaged tissue, including loose cartilage, bone spurs, and torn ligaments. Following arthroscopy, your doctor may prescribe physical therapy, which could take up to three months to complete.
Shoulder Arthroplasty is a procedure that involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one. The surgery is more complex than arthroscopy and is usually performed as a last resort when other methods have failed to relieve pain. The artificial joint used to replace the damaged one can be made of metal or plastic, called a “prosthesis.”
Broken Shoulder

A broken shoulder is a common injury that involves the bones of the upper arm or shoulder. The most common causes are a direct blow to the arm, such as by a boxer or martial artist, or falling on an outstretched arm.
If the person continues to attempt to lift objects after an Injury, this will further aggravate the injury and increase damage.
Over one-third of all breaks in any body part is in the shoulder area. The good news is that, with proper treatment and prompt medical attention, most people can return to all activities—even previously restricted—on their timetable.
Treatment Options for Broken Shoulder
Acute-care treatment for broken shoulder jibes with the description of the injury’s symptoms. It is important to understand that although most people may experience pain and swelling of the joint, it is generally not necessary to immobilize this area.
Rest does not work for a broken shoulder. Instead, the first steps are cold packs or ice, elevation, and pain medication. In the early stages of injury, the patient can continue to move and increase mobility within limits. It is important to maintain flexibility during this time.